Breast Rejuvenation
Breast Augmentation
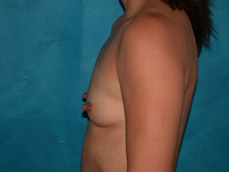
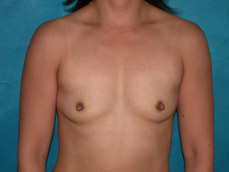
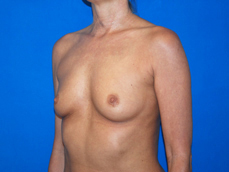
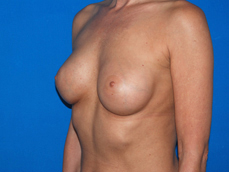
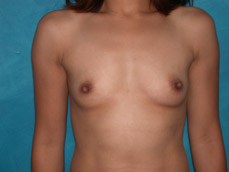
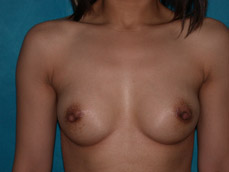
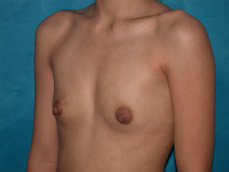
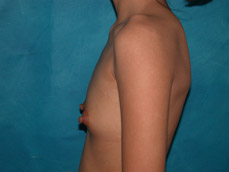
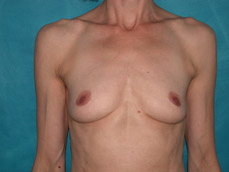
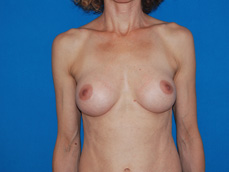
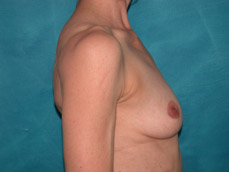
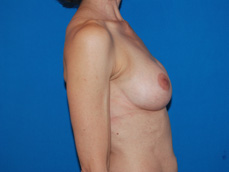
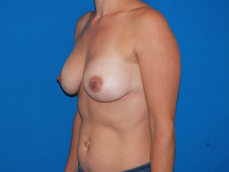
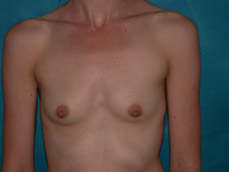
Breast augmentation is a plastic procedure that is designed to make the breasts fuller by placing an implant under the breast tissues. The result is a fuller breast. Dr. Chang advocates a natural breast augmentation and works with each of her patients to achieve their desired look. Dr. Chang’s patients include women who want to increase their breast size in order to achieve a better body proportion, women who want to fill out their breast volume for a more youthful look, and post-pregnancy mothers who want to bring their breasts back to their shape prior to having children. (Figures 1 and 2)

Figure 1

Figure 2
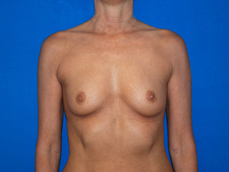
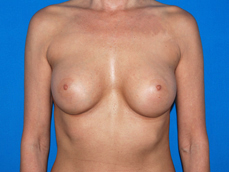
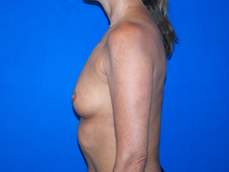
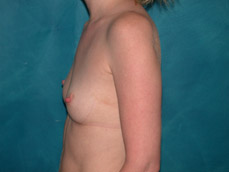
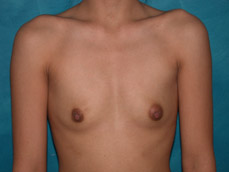
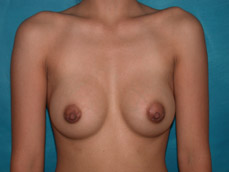
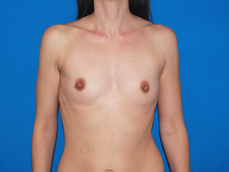
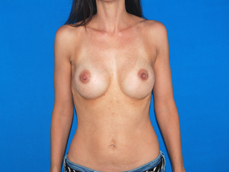
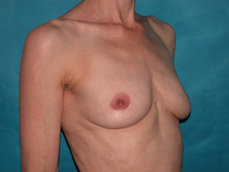
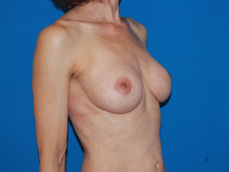
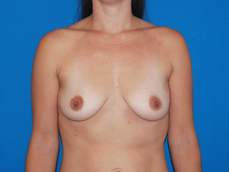
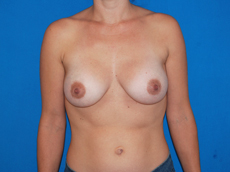
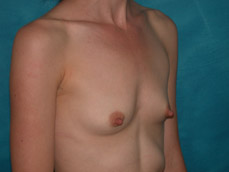
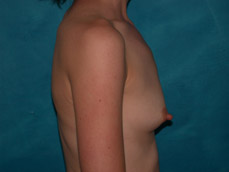
Breast augmentation surgery involves making an incision either under the fold of the breast, through the nipple, or under the armpit. (Figure 3) Through the incision, an implant is placed behind the breast tissue, and sometimes behind the breast tissue and the pectoralis major muscle, a large muscle on the chest. (Figure 4) The breast size is augmented by the implant, and a fuller look is achieved.
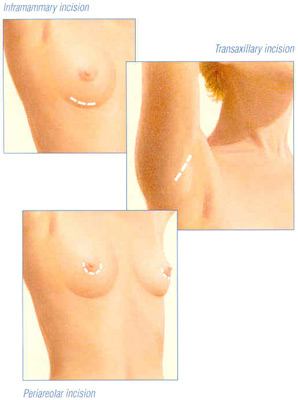
Figure 3
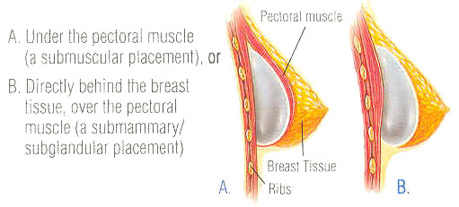
Figure 4
When contemplating breast augmentation, naturally one first thinks about size. In reality, there are many additional issues that one needs to consider in order to get the result that she desires. These include what implant type to use (silicone or saline), which incision to use (under the breast, through the nipple, or under the armpit), and which pocket to place the implant in on the chest wall (under the pectoralis major muscle, above the muscle, or partially under the muscle). All of these factors contribute to determining your overall result.
Implants today are available in silicone gel or saline fluid. In both of these types the shell of the implant is the same, made of a solid silicone. Both types of implants are fully approved by the FDA. The past controversies surrounding silicone implants have been largely discredited. In general, silicone implants have a superior look and feel in the body, particularly if one does not have a large amount of breast tissue available to cover the implant. This is because the silicone implant is made of a soft silicone gel that feels more similar to natural body tissue. The gelatinous material also gives the implant edges a softer look and feel when in the body. The obvious benefits of these implants must be weighed against the risks, however, for each individual. Silicone implants have a higher rate of capsular contracture, or hardening of the breasts. This is a physiologic process which causes the scar capsule which naturally forms around the implant to thicken and contract, thereby making the soft implant harder and more compact, like a baseball. This can be accompanied by some visible distortion. Luckily, this is a surgically correctable problem, and there are very few women who have continued capsular contracture. One can reduce the risk of encapsulation by placing the implant under the pectoralis major muscle during the breast augmentation.
Patients often are very concerned about the potential of implants to rupture and the safety of this occurrence. When saline implants rupture, the physiologic salt solution that makes up the filler of the implant simply dissolves in the body and visibly one breast becomes smaller than the other. Detection of rupture in a silicone implant requires a little more vigilance. Most often one notices some outward changes in the shape of the breast, and sometimes one can feel that the implant is distorted. Luckily, the vast majority of silicone ruptures stay contained within the scar tissue capsule around the implant, and the implant and silicone gel can easily be removed with very little “leakage” into the rest of the body. Imaging modalities, such as mammograms or MRI scans, can detect ruptures if there is any concern. The overall lifespan of both of these types of implants should be at least 10 years, and many women keep them for much longer. During your consultation, Dr. Chang will examine your breasts and help you to determine which implant type most achieves your goals and priorities.
When considering which pocket to place the implant in, whether above or below the muscle, it is important to realize that in a static photo, when the implants are done well, there should be virtually no discernable difference in the look. The advantage of going below the muscle is that it provides an extra layer of coverage over the implant in the cleavage area, and so one theoretically reduces her chances of seeing or feeling the implant in this area, especially if she is thin or has very little breast tissue to start with. The disadvantage of the submuscular approach is that because the implant lies beneath the muscle, with any activation of the pectoralis major muscles, there will be some distortion or movement of the implants beneath since they are getting moved slightly by the muscle above. Some women can find this distressing, particularly if they have very strong muscles or exercise a lot. For this reason, implants placed above the muscle in the subglandular position often look more natural when movement is introduced.
Other issues to consider include the fact that placing implants under the muscle can reduce your rate of capsular contracture, particularly if a silicone implant is used. And finally, for those patients with any history of breast cancer or a strong family history of breast cancer, Dr. Chang generally recommends a submuscular approach.
Some patients elect to have a partial submuscular approach to their breast augmentation. In this approach, only the part of the muscle which covers the innermost cleavage area is lifted. This approach avoids the motion issues associated with the traditional subpectoral implant placement while providing an extra layer of coverage over implant in the critical cleavage area. This approach, however, does not reduce one’s capsular contracture rate.
In regards to designing the scar, the most common approaches include under the fold, through the nipple, or under the armpit. The choice of which of these approaches is best for each patient is determined by a combination of anatomic considerations and personal preference. This will be discussed Dr. Chang on a personal basis during the consultation.
All of these choices and options can make choosing the “right” breast augmentation difficult and overwhelming. Dr. Chang, however, believes that each of her patients should understand all of the options, with the attendant risks and benefits, in order to make the best informed decision for herself. During your consultation Dr. Chang will help you sort out which combinations will best fit with your particular anatomy, lifestyle, and priorities. A customized approach will be developed for you in order to achieve the most natural and beautiful result for you.
Dr. Chang performs all of her breast augmentation surgeries in a fully licensed San Francisco hospital with board certified anesthesiologists. She recommends a general anesthetic for patient comfort and safety. The procedure generally lasts a few hours and patients can go home afterwards with supervision.
Recovery periods vary from person to person, but most people are feeling well enough to go back to work within a week. Dr. Chang recommends no heavy lifting, strenuous activity, or exercise for at least 2-3 weeks, after which there are no restrictions. During your recovery period, Dr. Chang will instruct you as to the best way to take care of your implants in order to prevent complications, such as hardening, so that you may optimize your results for the longest period possible.
Complications can occur, as with any procedure, and are important to consider when you are contemplating surgery. These can include bleeding, infections, loss of sensation on the breast or in the nipple, loss of the ability to breast feed, hardening of the implants, or anesthetic problems. Luckily, the vast majority of patients have uneventful surgical experiences and feel that their new look and renewed sense of confidence was well worth their efforts.
Breast Augmentation with silicone implant
Submuscular technique, areolar incision, silicone implant
Submuscular technique, inframammary fold incision, saline implant
Submuscular technique, inframammary fold incision, silicone implant
Subglandular technique, inframammary fold incision, silicone implant
Submuscular technique, areolar incision, silicone implant
Partial muscular strip, areolar incision, silicone implant
Subglandular technique, inframammary fold incision, saline implant
Submuscular technique, areolar incision, silicone implant
Post-pregnancy patient, subglandular technique, inframammary fold incision, silicone implant
Post-pregnancy patient, submuscular technique, inframammary fold incision, silicone implant
Post-pregancy patient, partial muscle strip, inframammary fold incision, silicone implant
Post-pregnancy patient, partial muscular strip, areolar incision, silicone implant
This gallery represents only a small selection of photos available for viewing. Additional before/after results are available at the time of your appointment.
Before and After Photos – individual results may vary